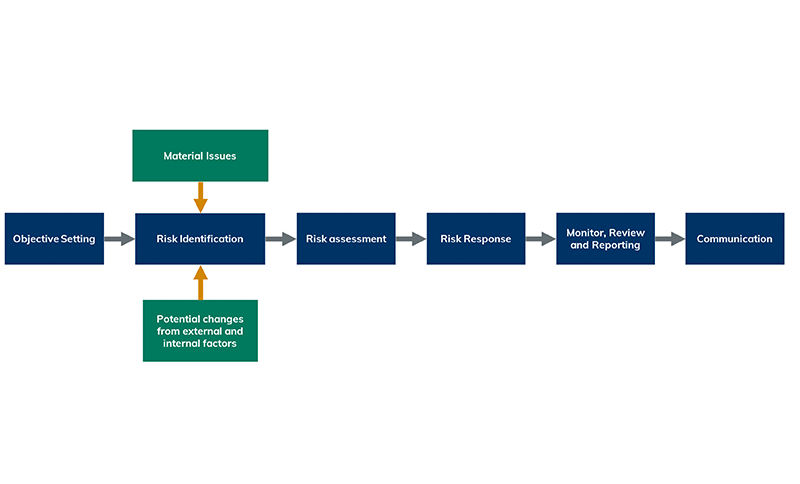
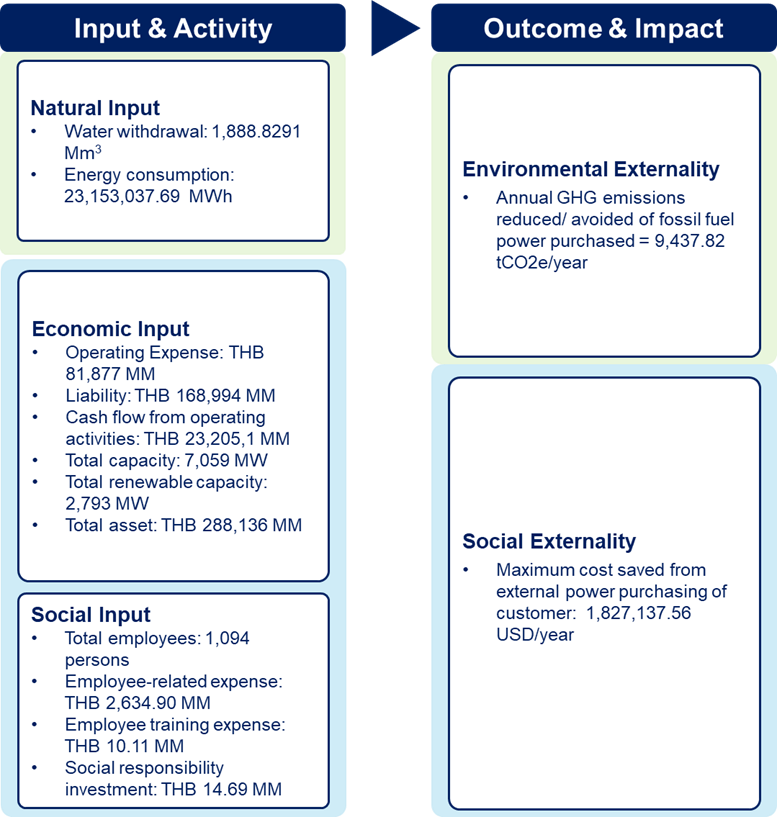
| Key Material Issue |
| Clean Energy Towards Net Zero |
- GPSC being one of the country’s leading service providers of clean energy, taking part in driving the attainment of Net Zero and climate change targets
- Attracting foreign investors into the energy industry
|
|
|
Government/public, customers, suppliers, investors, partners |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Energy (302-1, 302-3, 302-4)
- Emission (305-1, 305-2, 305-3, 305-4, 305-7)
|
|
- Supporting low-carbon businesses and innovations with promising future growth
- Encouraging the workforce to recognize the value of actions for Net Zero emissions
- Potential impact on investor and supplier confidence if there is a lack of clear management plans
|
|
|
Shareholders, investors, partners, customers, employees, suppliers |
- Promoting access to clean energy sources among consumers
- Potential cost and technological challenges in the clean energy transition
- Potential additional requirements for suppliers in their operations to ensure alignment with GPSC’s sustainability goals
|
|
|
Customers, Society and Communities |
| Environmental Management |
- Legal requirements that GPSC must follow, with direct impact on the corporate image and operations
|
|
|
Shareholders, Investors, Government Sector, Society and Communities, Customers |
|
- Strategy, Policies, and Practices (2-23, 2-24)
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Water (303-1, 303-2, 303-3, 303-4, 303-5)
- Emissions (305-7)
- Effluents and Waste (306-1, 306-2, 306-3, 306-4, 306-5)
- Environmental Compliance (307-1)
|
|
- Fostering trust between GPSC and communities and promoting quality of life enhancement in communities through good environmental management
- Responding to public policies
- Fostering a positive corporate image and confidence in the organization
- Managing community concerns over particulates emitted by power plants
- Potential cost increase due to more stringent environmental control measures
- Potential impact on business continuity due to lack of clear environmental management plans and enforcement of more stringent laws
|
|
|
Shareholders, Investors, Government Sector, Society and Communities, Customers |
| Capturing the Future Sustainability Market |
- Accommodating changing market trends, consumer needs, and public policies
- Potential challenges due to increased competition and more complex sustainability requirements
|
|
|
Shareholders, Investors, Government Sector, Customers, Suppliers |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Indirect Economic Impacts (203-1)
|
|
- Fostering cooperation for product development initiatives that create value and market opportunities for GPSC and its business partners
|
|
|
Partners |
| Corporate Governance & Compliance |
- Fostering confidence in GPSC’s business operations among stakeholders
- Exchanging knowledge on compliance and business code of conduct
- Promotion of continuous and sustainable growth through good corporate governance across all dimensions (ESG)
|
|
|
Shareholders, investors, partners, customers, suppliers |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Organization Profile (2-11)
- Governance (2-9, 2-10, 2-11, 2-13, 2-15, 2-23, 2-24, 2-25, 2-26, 2-27)
- Anti-corruption (205-3)
|
|
| Risk & Crisis Management |
- Fostering stakeholder confidence through systematic risk management for the prevention of potential impacts
- Potential new risks for operations and impacts on GPSC’s operating results and service provision, especially on overseas investment
- Impact on confidence in GPSC if there is a lack of proper management
|
|
|
Shareholders, Investors, Customers, Partners |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Governance (2-12, 2-13, 2-16, 2-23, 2-24)
|
|
| Employee-focused Organization |
- The role of employees in driving GPSC towards its targets
- Creating differentiation and competitive advantage
|
|
|
Shareholders, Investors, Employees |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Collective bargaining agreements (2-30)
- Diversity and Equal Opportunity (405-1, 405-2)
- Freedom of association and collective bargaining (407-1)
|
|
| |
- Career advancement, well-being, and good work environments for employees
- Reducing high turnover rates
- Potential lack of highly skilled personnel without sufficient human resource development
|
|
|
Suppliers, Employees |
| Fundamental Material Issue |
| Corporate Social Responsibility |
- Enhance brand reputation through meaningful contributions to societal well-being.
- Improve living standards for people in the surrounding communities through sustainable self-reliance.
- Employee participation in CSR activities enhances their skills, aligns them with the company’s strategies, and fosters organizational ownership and engagement.
|
|
|
Society and Communities, Employees, Shareholders, |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Local Communities (413-1, 413-2)
|
|
| Maintaining Availability and Reliability |
- Foster customer confidence, which continuously affects GPSC’s operating results
|
|
|
Shareholders, Investors, Customers, Employees |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- System Efficiency (EU-1, EU-2, EU-11)
- Demand Side Management (EU-10)
- Availability and Reliability (EU-28, EU-29, EU-30)
|
|
- Foster confidence, leading co-creation of business value
- Foster marketing stability for suppliers
- Reduces energy costs and enhances stakeholder trust.
- Lowers greenhouse gas emissions, benefiting the environment and society.
- Ensures reliable services, meeting customer and community needs.
|
|
|
Partners, Suppliers |
| Biodiversity |
- Protects ecosystems, benefiting local communities and future generations.
- Strengthens reputation among stakeholders through conservation efforts.
|
|
|
Shareholders, investors, government sector, society and communities |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Biodiversity (304-1, 304-2, 304-3, 304-4)
|
|
| Occupational Health and Safety |
- Ensures employee well-being, reducing workplace accidents and fostering trust.
- Promotes a safe and inclusive environment, benefiting society and local communities.
- Reduces environmental risks through safer operational practices.
|
|
|
Suppliers, Employees, Society and Communities |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Occupational Health and Safety (403-1, 403-2, 403-3, 403-4, 403-5, 403-6, 403-7, 403-9, 403-10, EU-25)
|
|
| Supply Chain Management |
- Impact GPSC’s operating results and operational continuity
- Impact the corporate image
- Ethical sourcing and transparency build trust with customers, investors, and partners.
- Promotes fair labor practices, benefiting communities and regulators.
|
|
|
Shareholders, Investors, Suppliers |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Health and Safety for Contractor and Subcontractor Employees (EU-17, EU-18)
|
|
| Being an Innovative Leader |
- Prevent disruption by new players and create operational strengths
- Be a leader in innovation from which partners can derive learning
- Drive growth with sustainable innovations, strengthening relationships with customers and investors.
- Enhance competitiveness and meets market demands.
|
|
|
Shareholder, Investors, Partners, Customers, Employees |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
|
|
- Enhance operational efficiency
- Enhance employees’ efficiency and give them time for skill development in accordance with their interest
- New technologies and innovations can help reduce employees' workload.
|
|
|
Employees |
- Impact the operating results through the development and procurement of innovation that can further enhance GPSC’s products and services in the future
- Poorly executed innovations may harm the environment and may reduce consumer loyalty and earnings growth stemming from innovative business areas.
|
|
|
Shareholder, Investors |
| Customer Relationship Management |
- Foster corporate credibility
- Maintain operational continuity
- Impact the corporate image
- Take proactive measures in maintaining and building customer relationships.
|
|
|
Partners, Customers |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
|
|
| Information Security/ Cybersecurity Governance |
- Protects data, maintaining trust with customers, employees, and investors.
- Adheres to privacy regulations, boosting stakeholder confidence.
- Effective breach management restores trust.
- Data breaches harm customer/employee trust and cause financial loss from lawsuits.
- Inconsistent cybersecurity causes loss in investor and public confidence.
|
|
|
Partners, Customers, Employees, Suppliers |
|
- Management Approach (3-1, 3-2, 3-3)
- Customer Privacy (418-1)
|
|