| 1. Economic recession, geopolitical tensions and war risks/td> |
High |
2025 |
The situation of war and political conflict, economic slowdown, fluctuations in the financial and capital markets, and production-consumption sector from the fragile economic conditions have resulted in limitations affecting GPSC's business operations and performance, as well as the GPSC group of companies. |
- Impact from the increased adjustment of energy fuel prices has led to GPSC experiencing adverse effects on business performance that do not align with the planned objectives.
- The economic slowdown and trade regulation impact have reduced demand for GPSC products.
- The impact from financial and treasury policy management under the inflation control conditions and economic stability at the international level affects GPSC's financial costs and expenses.
- Political risks at regional and national levels pose obstacles to GPSC's business operations under its growth strategy.
|
- Managing the impact on business performance through fuel price formulas used in electricity production and distribution contracts, along with plant optimization operations, production, and distribution improvements, and coordination with relevant external agencies.
- Coordinating cooperation between customers/partners to maintain production and electricity delivery stability.
- Risk management and impact mitigation through the Raw Material Price and Financial Hedging Committee, as well as monitoring interest rate situations and financial costs to find suitable financial instruments.
- Managing risks and impacts from investment project selection, short and long-term evaluation, business partnership establishment, in-depth business environment study through GPSC personnel in the area, and considering Exit Strategy in appropriate situations.
|
| 2. Power and Energy Interfere Risk |
High |
2025 |
Government policies to stabilize electricity prices to alleviate the burden on consumers have impacted electricity producers and GPSC due to inconsistencies between energy fuel prices and electricity prices.
|
- The impact of electricity price stabilization policies by the government, which do not reflect the actual cost, has resulted in adverse effects on GPSC's business performance that do not align with the planned objectives.
|
- Seeking ways to reduce overall production costs, coupled with maintaining and improving production efficiency and stability appropriately.
- Overall production and distribution optimization (Plant Optimization).
|
| 3. Climate Regulation and Climate Action Risk |
medium |
2030 |
As international commitments, including those by Thailand, aim to address the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, with Thailand setting a target to reduce emissions by 40% by the year 2030, it poses conditions affecting the current operations and business of GPSC. This necessitates seeking ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions under the management of production from stable fossil fuels, essential for electricity generation to support industrial usage. This includes financial management and cost from policies supporting investments in clean fuel businesses, alongside maintaining business performance to respond to shareholders and stakeholders. |
- Measures to prevent trade barriers through taxes and additional expenses in products with higher greenhouse gas emissions than specified levels, affecting both customers and possibly leading to reduced product purchases and increased expenses for GPSC.
|
Accelerating production efficiency, energy fuel usage, investing in renewable energy, developing new business models for clean energy procurement, and certification of clean energy emissions. Studying and developing new energy utilization technologies with low greenhouse gas emissions. Exploring technologies for carbon capture and storage.
|
| 4. Power and Steam Production and Synchronization Risk |
High |
2028 |
Currently, EGAT is in the process of upgrading the electricity transmission system in the Rayong province and the eastern region to address the issue of high Fault Level, which exceeds the specified limit. Consequently, all newly commissioned and SPP Replacement power plants of GPSC are not permitted to connect to EGAT's transmission system. |
- GPSC faces constraints in production management and operation during certain periods.
- Production and distribution costs have increased while revenue remains the same under product sales agreements.
|
- Analyzing and coordinating technical studies with EGAT to address connection issues.
- Managing maintenance to increase production and distribution efficiency and reduce downtime of power generation units.
- Managing operation and maintenance downtime in conjunction with energy procurement planning with customers.
- Plant optimization to manage overall production efficiency.
- Collaborating with EGAT to procure additional electricity during power generation maintenance periods.
|
| 5. Changed Rules and Regulations impacted to GPSC Business Expansion |
High |
2027 |
As for the energy transition agenda in the global context, the increased challenge of renewable energy generation and distribution has become an attractive topic. Adopting the change regarding this trend leads to new challenges for the competitive market and emerging business. Likewise, this has been addressed as an emerging risk related to the unforeseen uncertainty of the new and restrict coming regulations, policies, and measures in Thailand within 3-5 years. Particularly, the electricity tariff mechanism. An emerging risk driven from the changed in rules and regulation derived from energy transitions is recognized to potentially cause direct business impact to GPSC. |
- The competitive market is also one of the challenges for new renewable energy businesses of GPSC in the market share context. In a highly competitive market, companies have to compete for customers, and they may have to lower their prices or offer better products or services to attract customers away from their competitors. This can result in a decline in market share and revenue for GPSC if the company is unable or unwilling to adapt to the changing market conditions.
- The applicable electricity tariff from newly changed policies and regulations can influentially impact GPSC as generated revenue, which is uncertain, particularly imposing the electricity fee through the UGT mechanisms.
- Demanding green products from customers who were impacted by energy transition could effectively result in an increase of company capital investment to seek alternative energy and/or clean technologies for more sustainable solutions of power producing.
|
- Increase the share of renewable energy assets in the generation mix through targeted investments, partnerships, and acquisitions. Prioritize scalable and dispatchable RE technologies, such as solar-plus-storage, to improve resilience and customer attractiveness under future market conditions.
- Develop adaptive pricing models that incorporate projected regulatory scenarios, enabling GPSC to maintain margin stability under various tariff structures. Explore long-term green PPAs with off-takers seeking predictable green energy pricing.
- Conduct scenario-based impact assessments to quantify financial exposure under different regulatory.
- Establish a financial buffer or green investment fund to absorb transitional shocks and capitalize on new opportunities.
- Continuously developing alternative technologies for lower carbon emissions i.e. CCS, Hydrogen Production, Nuclear SMR, etc.
|
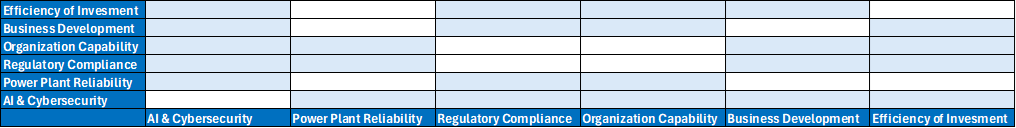
| 6. Digital Transformation and AI Adoption Risk |
High |
2030 |
The growth and development of new technology pose substantial risks to businesses worldwide. In the context of electric utilities, digital and AI driven technologies such as energy trading platforms, grid optimization tools, and digital twins play a crucial role in long-term business transformation. The impact of these technologies is uncertain and may not pose an immediate threat. It could potentially lead to market competitiveness failure if GPSC is not prepared for adoption and does not remain resilient. Such risks could impact GPSC’s operational efficiency, reduce workforce capabilities, and slow its ability to innovate and adapt to evolving business needs. Moreover, these technologies introduce new cyber-attack risks that could disrupt systems and data. Recognizing these challenges, GPSC executes its digital transformation management, integrating AI into strategy and operating process as well as strengthening cyber defenses to stay resilient and competitive in a changing energy landscape. |
- Failing behind to enhance AI technologies advancement in power business value chain would mean losing ground to more agile compared to competitors, missing growth opportunities in areas e.g. VPPs and smart grids, and gradually lowering market share and long-term profitability.
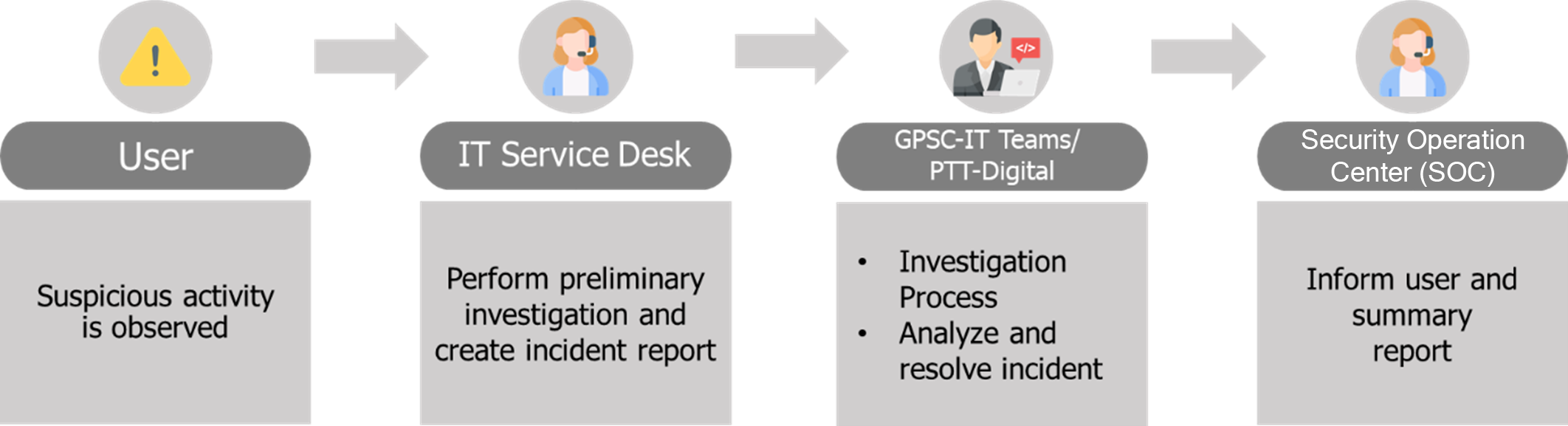
- Increasing use of digital and AI driven technologies could expose GPSC to cyber-attacks targeting these advanced systems. Without robust cyber defenses and proactive monitoring, cyber threats may cause operational disruptions, data breaches, and serious reputational and financial damage.
- Rapid adoption of digital and AI driven technologies requires specialized skills in data analytics, AI model management, and digital system integration. Without proactive workforce upskilling and talent acquisition, GPSC may face a shortage of qualified personnel, leading to slower implementation of new technologies and reduced innovation capacity over time.
|
- Drive and execute continuous digital transformation strategy and AI adoption to improve process efficiency, scalability, and support the company’s strategic goals, develop clear milestones for digital transformation and AI-driven adoption across key processes e.g. asset management, energy dispatch, predictive maintenance, and demand response including resource allocation and implementation plans.
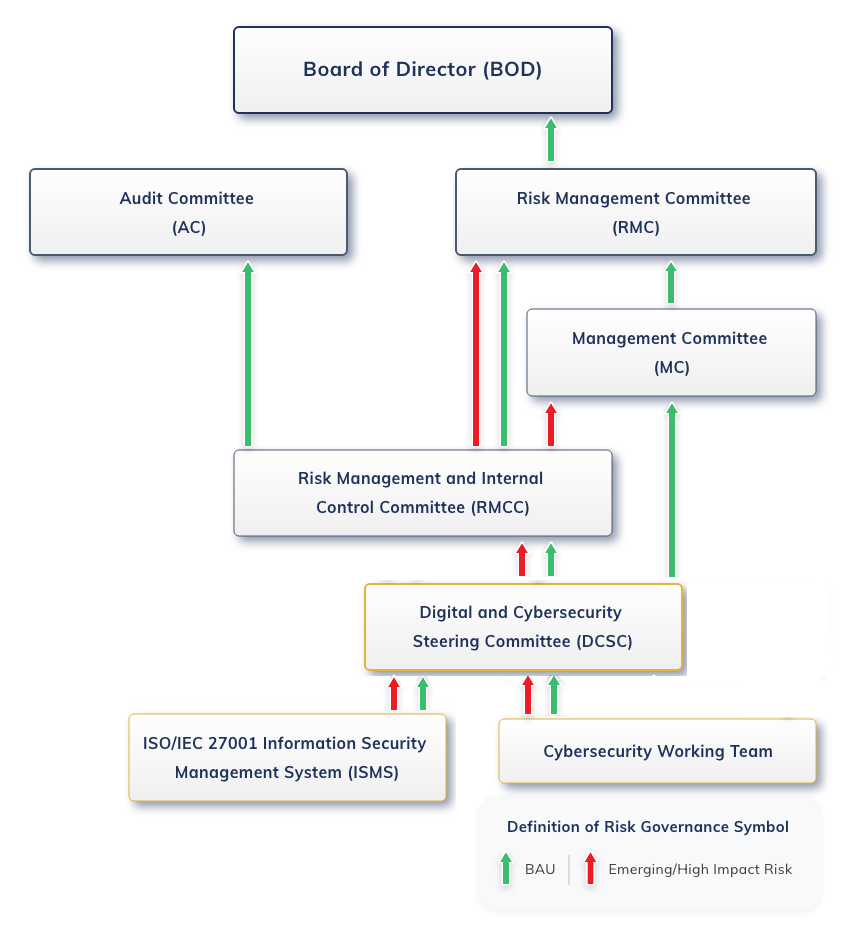
- Implement a robust cybersecurity improvement plan and closely monitor its effectiveness to ensure the protection of company data, data breach, OT & IT systems, and business continuity.
- Develop workforce capabilities and expertise in digital, AI transformation, and cybersecurity, enhance tools and systems to strengthen innovation and data protection, and ensure overall organizational readiness to support continuous improvement, boost employee engagement, and sustain long-term business growth.
|
| 7. New Technology / Energy Advancement Risk |
High |
2032 |
The energy sector plays a vital role in the transition toward a low-carbon economy and sustainability. Conventional energy is being phased out and replaced by new advancements in energy technology. The accelerating pace of new energy, including solid-state batteries, SMR, H2–based energy, ammonia, and CCUS, poses a new and significant risk to the global energy sector including GPSC. These technologies have the potential to reshape the energy landscape, driving the transition from traditional centralized utilities to micro-decentralized, self-optimizing energy ecosystems. For GPSC, this could result in long-term shifts in the market and changes in customer expectations. This risk is still emerging as these technologies are in the early stages of development, and their impacts are yet to be fully realized. GPSC is preparing its business model called “S-Curve” to ensure the ability to adapt on these changes as a new pathway and integrate new energy solutions into its operations If GPSC delays implementing its S-Curve strategy and new energy solutions, the company may face penalties, fines, and rising compliance costs (e.g., carbon taxes) as stricter GHG emissions and sustainability regulations take effect. Failure to adapt could also expose the company to legal risks and greater financial pressures. |
- GPSC risks losing its market position if it fails to adapt to the shift toward new energy advancements. As competitors embrace emerging technologies and decentralization continues to disrupt traditional utility-based business models, GPSC could lose its competitive edge, leading to declining revenue and market share as customers increasingly demand more flexible, efficient, and sustainable solutions. To remain competitive, GPSC must proactively embrace platform-based, service-oriented, and data-driven approaches that align with evolving market expectations and sustainability goals.
- If GPSC delays implementing its S-Curve strategy and new energy solutions, the company may face penalties, fines, and rising compliance costs (e.g., carbon taxes) as stricter GHG emissions and sustainability regulations take effect. Failure to adapt could also expose the company to legal risks and greater financial pressures.
|
- Develop next-generation technologies such as solid-state batteries, hydrogen-based solutions, ammonia, CCUS, and nuclear microreactors (e.g., SMR), and secure strategic partnerships to accelerate integration and maintain competitiveness.
- Evolve GPSC’s business model under S3 and S4 Strategies to be service-oriented and data-centric, integrating flexible energy solutions such as energy decentralization that combine renewable generation and energy storage for optimized, on-demand supply.
- Govern the study to long-term R&D in emerging energy technologies and invest in infrastructure for decentralized energy systems to ensure GPSC is well-positioned for future energy solutions.
- Collaborate with energy innovators and tech companies to adopt new technologies, reducing financial burdens while staying ahead in the evolving energy market.
- Engage with related government authorities to support the relevant policy/ regulation/ to push forward new technologies to implementation phase.
|